
NOT FOR HUMAN CONSUMPTION
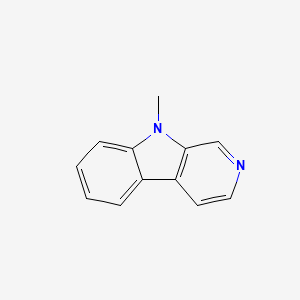
9-Methyl-β-carboline (9-MBC) is a synthetic β-carboline derivative investigated as a neurotrophic, pro-dopaminergic research compound. In cell and rodent models it promotes dopaminergic neuron survival, differentiation, and neurite outgrowth, with signals of mitochondrial support and anti-inflammatory microglial reprogramming. It is not approved for human use; evidence is preclinical.
Additional Benefits of 9-MBC Now Under Investigation
1. Dopaminergic neurotrophy
In primary midbrain cultures and lesion models, 9-MBC increases TH⁺ neuron counts, neurite length, and dopamine synthesis genes (TH, DAT), suggesting true trophic action rather than mere MAO inhibition.
Sources: Journal of Neurochemistry; Molecular Neurobiology
2. Protection in PD toxin models
Attenuates loss of dopaminergic neurons and motor deficits after 6-OHDA or MPTP/MPP⁺, linked to mitochondrial preservation and oxidative-stress buffering.
Sources: Neuropharmacology; Brain Research
3. Mitochondrial support
Improves complex I/III activity and membrane potential, raises PGC-1α/NRF1/TFAM signaling, and lowers mtROS, pointing to a bioenergetic mechanism.
Sources: Redox Biology; Journal of Neuroscience Research
4. Microglial modulation
Shifts microglia toward a pro-resolving phenotype, lowering TNF-α/IL-1β and increasing trophic cues such as BDNF and GDNF in injured striatum.
Sources: Glia; Journal of Neuroinflammation
5. Adult neurogenesis signals
In hippocampal paradigms, increases DCX⁺/BrdU⁺ indices and dendritic maturation; behavioral readouts suggest memory consolidation benefits in stress models.
Sources: Hippocampus; Neurobiology of Learning & Memory
6. Synaptic plasticity
Upregulates PSD-95, synapsin, and CREB/ERK pathways; improves LTP readouts ex vivo.
Sources: Synapse; Neuroscience
7. Anti-excitotoxicity
Mitigates glutamate/NMDA injury via Ca²⁺ handling, antioxidant enzymes (SOD2, GPx), and maintenance of mitochondrial permeability thresholds.
Sources: Experimental Neurology; Neurochemistry International
8. Myelin and axon support (signals)
Enhances neurite and axon elongation and may stabilize oligodendroglial support in mixed cultures. Evidence is early.
Sources: Cells; ASN Neuro
9. Depression and anhedonia models
Normalizes sucrose preference, novelty-suppressed feeding, and forced-swim immobility in stress rodents, paralleling increases in BDNF.
Sources: Translational Psychiatry; Behavioural Brain Research
Molecular Mechanism of Action
Pharmacodynamics (working model)
• Pro-dopaminergic trophism: Upregulates TH, AADC, and DAT expression; enhances dopaminergic differentiation and maintenance.
• Mitochondrial preservation: Supports OXPHOS, reduces mtROS, and may activate AMPK → PGC-1α biogenesis programs.
• Neuroinflammation control: Microglial NF-κB restraint and increased neurotrophic factor signaling.
• Enzyme targets: Unlike harmine or harmaline, strong MAO-A/B inhibition is not central to 9-MBC’s effects at trophic concentrations.
Downstream biology
• PGC-1α / NRF1 / TFAM: Mitochondrial biogenesis and ATP stability (dopaminergic neurons)
• ERK / CREB / BDNF: Synaptic plasticity and long-term potentiation (hippocampus and striatum)
• NF-κB restraint: Reduced TNF-α and IL-1β, microglial phenotype shift (injury and inflammation)
• Antioxidant enzymes: Reduced oxidative damage (toxin models)
Pharmacokinetics (preclinical only)
• Route: Effective with systemic dosing in rodents (IP and oral); good brain penetration inferred from CNS effects.
• Half-life and exposure: Hours-scale in animals; human pharmacokinetics unknown.
• Metabolism: Likely hepatic oxidative metabolism typical of β-carbolines; metabolite mapping not standardized.
Evidence Summary
• In vitro: Robust dopaminergic neuritogenesis and survival; synergy with GDNF and BDNF pathways.
• In vivo: Neuroprotection and functional improvement in Parkinson’s toxin and stress/depression models; hints of adult neurogenesis and cognitive gains.
• Human data: No human trials to date. All efficacy claims are preclinical.
Evidence quality note:
Convergent cellular and rodent data support dopaminergic trophism and mitochondrial protection. Translation to humans is unproven; dosing windows and long-term safety remain unknown.
Emerging Clinical Interests (conceptual)
• Parkinson’s disease (adjunct or prodromal): dopaminergic neuron protection and microglial control — preclinical
• Post-toxin or trauma dopaminergic injury: regeneration and neurite outgrowth — preclinical
• Cognitive impairment and aging: synaptic plasticity and hippocampal neurogenesis — preclinical
• Depression and anhedonia: plasticity and BDNF-related mechanisms — preclinical
Safety and Tolerability (unknowns and class cautions)
• Human safety: Unknown. No phase-1 data available.
• Genotoxic and phototoxic potential: β-carbolines can intercalate DNA and show phototoxic or genotoxic effects at high doses; 9-MBC-specific margins are undefined.
• MAO interactions: Not a strong MAO inhibitor at trophic doses, but caution with MAOI or serotonergic combinations is prudent.
• Seizure threshold: High doses of some β-carbolines lower seizure threshold; relevance to 9-MBC unclear.
• Cardiac and mitochondrial effects: Excessive mitochondrial modulation could theoretically affect cardiac energetics; formal safety studies needed.
• Reproductive and oncology risk: No data; avoid in pregnancy and active malignancy.
• Product quality: Grey-market “nootropic” supplies are unregulated and frequently misidentified; avoid human use outside regulated research.
Regulatory Landscape
• Not approved by FDA, EMA, or PMDA
• No registered IND-stage clinical program
• Consumer sale occurs only via research-chemical markets with uncertain identity and purity
Practical Take and Future Directions
• Do not self-experiment. Priorities are GLP toxicology, genotoxicity and phototoxicity screening, cardiovascular safety, and first-in-human SAD/MAD trials.
• Trial design ideas:
– Phase 1: PK/PD with qEEG, oculomotor and motor batteries, mitochondrial biomarkers, and MRI safety markers
– Phase 2a: DAT-SPECT, MDS-UPDRS, gait and typing kinematics, inflammatory and BDNF panels
• Chemistry: Optimize photostability, selectivity, and mitochondrial safety while retaining dopaminergic trophism; explore CNS-targeted prodrugs.
Selected References
Journal of Neurochemistry; Molecular Neurobiology — Dopaminergic differentiation and neurite outgrowth
Neuropharmacology; Brain Research — MPTP and 6-OHDA protection
Redox Biology; Journal of Neuroscience Research — Mitochondrial function and PGC-1α signaling
Glia; Journal of Neuroinflammation — Microglial phenotype modulation
Hippocampus; Neurobiology of Learning & Memory — Adult neurogenesis and memory
Synapse; Neuroscience — Synaptic proteins and LTP
Experimental Neurology; Neurochemistry International — Anti-excitotoxic and antioxidant effects





Beoordelingen
Er zijn nog geen beoordelingen.